AD is the most common form of dementia worldwide and accounts for about 60-80% of the cases
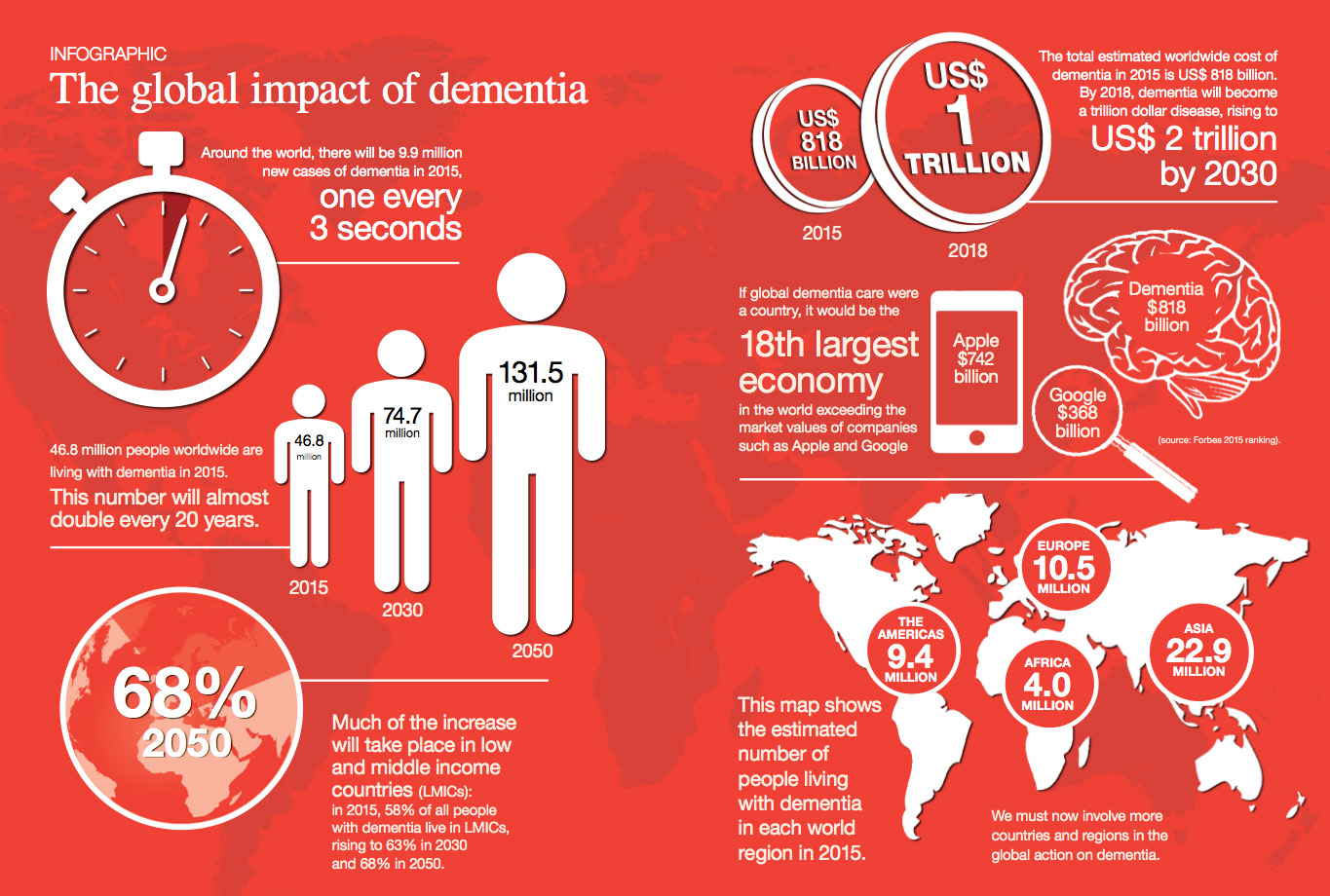
The total estimated worldwide cost of AD and other dementias in 2015 was $818 billion and estimated to rise to $2 trillion by 2030
AD affects 7-10% of individuals over the age of 65 and 40-50% of persons over the age of 80
An estimated 46.8 million people worldwide are living with dementia in 2015 and over 74.7 million projected to develop dementia by 2030 and 131.5 million by 2050
The fastest growth of the elderly population is presently taking place in China, India, and other regions of Southeast Asia
An estimated 5.5 million Americans are currently diagnosed with AD, and AD is the 6th leading cause of death in the U.S. (1 in 3 seniors dies of AD or another related dementia)
Direct and indirect costs of AD and other dementias for 2013 in the U.S. was over $203 billion ($1.2 trillion by 2050), including $142 billion for Medicare and Medicaid” with the statement “The direct and indirect costs of AD and other dementias for 2015 in the U.S. were estimated to be $226 billion ($1.1 trillion by 2050), including $154 billion for Medicare and Medicaid
In the U.S. alone, introduction of a drug that delayed the onset of AD by 5 years would result in savings of $150 billion over the first 20 years of use
Therefore, due to the ever increasing size of the aging population globally, AD and other dementias are, and will continue to be a major socioeconomic concern tremendous unmet medical need worldwide
Neurotrauma is one of the most common injuries in contact sports and military conflicts
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 1.6 to 3.8 million sports-related concussions or mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBIs) occur annually in the US
TBI is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in people under the age of 45 and contributes to 30.5% of the injury related deaths in the US
Recent estimates indicate that 10 to 20% of the 2.5 million US military service members deployed to Iraq and Afghanistan may be affected by TBI and the majority of these injuries are associated with blast exposure
The US Department of Defense (DoD) has labeled blast-induced TBI (bTBI) as the “signature injury” of the recent wars in Iraq and Afghanistan
The estimated annual cost of treatment for bTBI in the US is $2.5 billion
Repeated concussions or head trauma frequently leads to a neurodegenerative condition known as chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) with professional athletes in contact sports, such as American football, ice hockey, soccer, wrestling, and boxing, and soldiers being the two populations at greatest risk for developing CTE
In a recent study conducted at the Department of Veterans Affairs’ brain repository in Bedford, MA, of the postmortem brain tissue of 128 former football players (i.e., professionals, semi-professionals, college and high school players), it was observed that 101 players tested positive for CTE. In other words, 78.9% of all the football players and 96.2% of the former NFL players in the study suffered from the disease.